Till 2021, China has signed agreements on agricultural cooperation with 86 BRI countries and established stable working mechanisms with more than half of them, and has jointly invested in more than 820 state-funded agricultural projects with an investment stock of more than US $17 billion along the Belt and Road. The regions along the Belt and Road are rich in grain resources, with a huge market for the grain trade, as the world's main production area of rice and wheat. Cross-border and trans-regional cooperation in agriculture between China and countries along the Belt and Road is increasing, as integrated utilisation of global agricultural resources is an effective approach to ensure grain security and end hunger and poverty in both China and the B&R countries. From the perspective of embracing overseas investment, the global supply chain built under the Belt and Road Initiative will make a big difference in balancing the allocation of China's agricultural resources. Under the Initiative, agricultural cooperation can be a good foothold for B&R countries to build a community of common interests and destiny.

Image: 19th China-ASEAN Expo and Investment Summit (CGTN)
Agriculture policies
-
[China] Jointly Promoting Agricultural Cooperation on the Belt and Road
The Chinese government proposes that Belt and Road countries seek complementarities through the stronger connection of strategies on agricultural cooperation, on the basis of the principle of mutual consultation, joint efforts and shared interests and concepts of peace and cooperation, openness and inclusiveness, mutual learning and benefits under the Belt and Road Initiative, accommodate interests and concerns of all parties involved, proceed from science and technology, focus on policy coordination, facilities connectivity, unimpeded trade, financial integration, and people-to-people bonds to deepen collaborations on optimal technologies, priority products, and trade and investment along the six economic corridors (new Eurasian Land Bridge, China-Mongolia-Russia, China-Central Asia-West Asia, China-Indochina Peninsula, China-Pakistan, and Bangladesh-China-India-Myanmar), and work jointly for a full-fledged and wide-ranged new cooperative relationship.
-
[Indonesia] Government Regulation 47/2012 on Social and Environmental Responsibility
The government of Indonesia issued Government Regulation 47/2012 on Social and Environmental Responsibility for Limited Liability Companies. This regulation states that companies operating in the field of and/or related to natural resources are obligated to conduct social and environmentally responsible activities and they must be included in the annual budget plan. Also, these activities must be published in the annual report and reported at the General Meeting of Shareholders[1].
[1] Layukallo, R., Fanggidae, V., & Ningrum, D. R. (2016). Mapping of Policies and Stakeholders in Foreign Direct Investment in Indonesia’s Agriculture Sector. Perkumpulan PRAKARSA.
-
[Indonesia] ‘Investment Positive List’
In March 2021, Indonesia adopted a so-called ‘Investment Positive List’ (replacing the previous “Negative List”) through the issuance of Presidential Regulation No. 10 of 2021 (as amended by Presidential Regulation No. 49 of 2021) – as the implementing regulation of Law No. 11 of 2020 regarding Job Creation (also known as the Omnibus Law) (Positive List).
Whilst not subject to screening or prior approval, FDIs are prohibited in the following six strategic sectors (business fields closed for investment):
- cultivation and processing of controlled substances;
- gambling and/or casino activities;
- fishing of species listed in Appendix I of the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora;
- utilization or collection of coral for building materials, aquariums, or souvenirs, as well as live or recently dead coral;
- chemical weapons manufacturing; and chemical industry materials and processing of hazardous materials to the ozone layer.
-
[Cambodia] FDI for Agribusiness Process in Cambodia
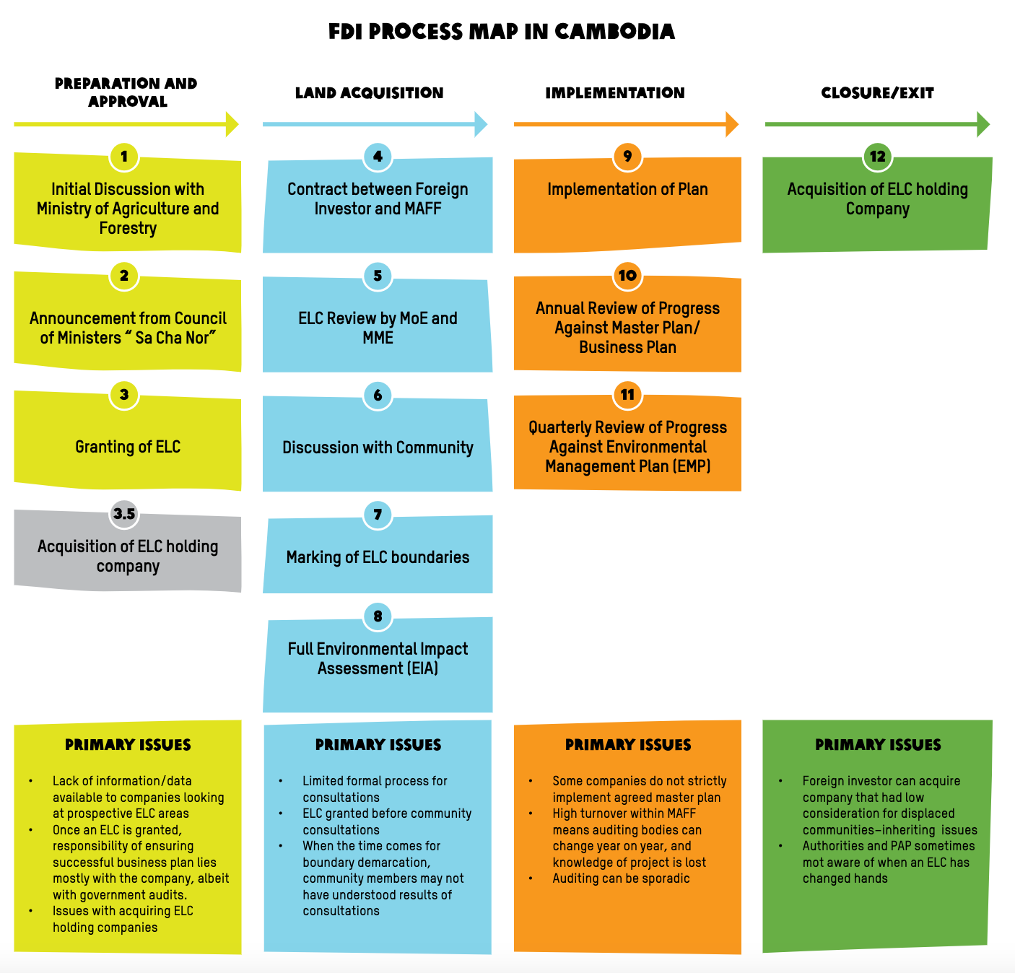
Source: Oxfam (2019)
-
[China] Third Belt and Road Forum for International Cooperation
The Third Belt and Road Forum for International Cooperation was held in Beijing in October 2023, with the theme of "High-quality Belt and Road Cooperation: Together for Common Development and Prosperity". China’s President Xi Jinping convened the Third Belt and Road Forum for International Cooperation, marking the tenth anniversary of the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
Highlighting the BRI’s successes in building a global network of connectivity that includes economic corridors, international transportation routes, and an information highway, as well as railways, roads, airports, ports, pipelines, and power grids, China's President Xi Jinping announced eight major steps China will take in support of high-quality Belt and Road cooperation:
- Build a multidimensional Belt and Road connectivity network;
- Support an open world economy;
- Carry out practical cooperation;
- Promote green development;
- Advance scientific and technological innovation;
- Support people-to-people exchanges;
- Promote integrity-based Belt and Road cooperation; and
- Strengthen institution building for international Belt and Road cooperation.

Source: beltandroadforum.org
-
ASEAN-China Joint Statement on Deepening Agricultural Cooperation
At the 26th ASEAN-China Summit in Jakarta, Republic of Indonesia, on 6 September 2023, Member States of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) and the People’s Republic of China, launched the Joint Statement on Deepening Agricultural Cooperation. In the past several years, important consensus on agricultural cooperation has been achieved in documents such as the ASEAN-China Strategic Partnership Vision 2030, the Joint Statement of the ASEAN-China Special Summit to Commemorate the 30th Anniversary of ASEANChina Dialogue Relations, and the ANNEX to the ASEAN-China Plan of Action 2021- 2025: Advancing ASEAN-China Comprehensive Strategic Partnership. This joint statement reaffirms that agriculture is a fundamental sector that bears upon food security, social stability, economic prosperity, and ecological conservation.
In order to make agriculture a new growth engine of ASEAN-China cooperation, so as to contribute to the ASEAN-China Comprehensive Strategic Partnership and the realization of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, ASEAN and China agree to:
- Improve agricultural cooperation mechanisms;
- Built more resilient regional agri-food systems;
- Promote sustainable, resilient, circular and low-carbon agriculture;
- Develop smart agriculture and digital villages;
- Deepen cooperation on agricultural supply chains;
- Increase stakeholders’ participation in the regional agricultural cooperation.
Full document: Chinese English

Picture: China Daily